When the environmental temperature is very low, the body loses more heat than it can generate. This can lead to dangerous health conditions like frostbites and hypothermia
WHAT IS HYPOTHERMIA?
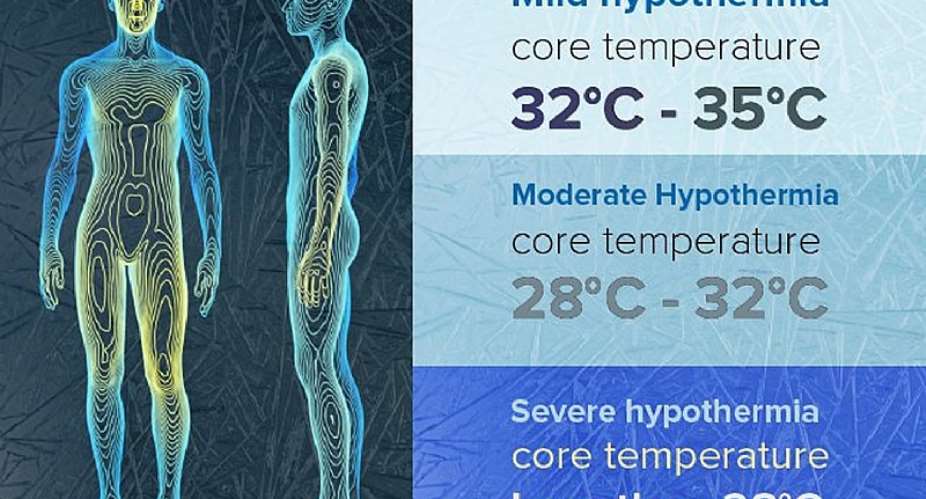
Hypothermia means abnormally low core body temperature. The normal body temperature is about 37 degree centigrade (*C). Below 36*C, cold begins to set in.
Hypothermia may occur when the body is exposed to very cold temperatures for long periods. In very cold weather, the body loses more heat than it generates. With time, the body uses up all the stored energy, and the core body temperature starts to drop rapidly.
Hypothermia slows the brain function; it makes affected person not think clearly, they may be unaware of their situation and they may not able to do anything about it.
Hypothermia could lead to internal organs (brain, heart lungs) failure and death if left untreated promptly
RISK FACTORS FOR HYPOTHERMIA
- . Everyone, but more common in those at Extremes of age: babies and older perssons, who sleeping in cold rooms.
- . Those who work or stay outdoors for long periods: hikers, homeless, winter sports enthusiasts,
- . Those who drink Alcohol or those who use drugs like nicotine that tend to reduce blood flow.
- . Living in homes with inadequate heating and clothing
- . Winter/Freezing weather
- . Inadequate clothing or tight clothes
- . Kids and Older adults who sleep in cold rooms
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF HYPOTHERMIA
The signs and symptoms depend on severity of the hypothermia. Below 36*C, cold set in. At 34*C Organ malfunctions begin.
- . Shivering: shivering is the first sign that the body is losing heat.
- . Cold feet and hands
- . Cold pale or blue skin
- . Lack of coordination, fumbling hands
- . Slurred speech
- . Slow breathing
- . Irregular, slow and weak pulses
- . Mental confusion or sleepiness
FROSTBITE
Frostbite occurs when the fluid in the colder skin areas freezes, and the ice crystals formed obstruct blood flow to those areas, which could result in damage and local skin death.
The skin gets cold when it is exposed to freezing cold temperature and cold wind.
Blood flow to the skin, decreases in low ambient temperatures.
Normal skin blood flow is 200-250ml/minute.
At 15*C the flow decreases to 20-50mls/minute.
At 10*C, skin sensation is lost
Below 0*C, there is negligible skin blood flow and freezing starts.
RISK FACTORS FOR FROSTBITE.
- Genetically, Blacks get frostbite earlier than whites.
- The risk factors are the same as the risks for hypothermia.
- People with poor circulation
- People who use nicotine and similar drugs that tend to reduce blood flow
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF FROSTBITE
Areas more susceptible to frostbite: Nose, Cheeks, Chin, Ears, Toes, Fingers (they are affected often)
Local Pain, stinging, throbbing sensations and redness are the first symptom and sign
The area:
becomes Pale, feels firm /waxy and Numb.
Because of the numbness, the person with frostbite may be unaware of that. Somebody points it to them,
COMPLICATION FROSTBITE
Damaged skin may slough off. Healing is slow, (it may take 6-12 months to heal) and scars usually form.
Sometimes frostbite leads to amputation of toes and fingers.
HOW TO AVOID HYPOTHERMIA AND FROSTBITE
COVER YOUR BODY IN WARM, DRY, LOOSE CLOTHES
- Cotton clothes are for warm weather; they are not helpful in cold weather conditions.
- Cotton clothes do not hold heat, the clothes make the body lose heat faster. Cotton does so by allowing sweat to evaporate rapidly. Anytime sweat evaporates, heat is lost from the body.
- In the cold weather, we need clothes that retain sweat
- Clothes that can hold heat include: WOOL, SILK, POLYPROPENE.
- Depending on the weather temperature, a layer-up of clothing help protect our bodies from cold weather conditions.
- Three clothing layers can protect the body from severely cold weather.
INNER LAYER:
Fabrics that can hold heat: synthetic materials like Polypropylene, Wool, Silk. These materials hold more heat than cotton.
MIDDLE LAYER:
Natural fiber like wool, fleece, goose down, insulate the body from heat losses
OUTER LAYER:
Water and wind resistant materials that shield the body from inclement weather conditions and decrease bodily heat losses.
PHYSICAL ACTIVITY IN COLD/FREEZING WEATHER.
One can always work outside in the cold weather, if they dress up properly.
Working out in cold weather boost the immune system, provided you breathe warm air, by covering your nose. If you do not cover your nose, you may catch the cold virus.
To avoid hypothermia and frostbites, the key point is Dress Warm; Stay Dry.
For Frostbite prevention, we need to cover:
The nose, cheeks, chin: cover your face with face mask or scarf. It warms the inhaled air.
Ears: a heavy wool or fleece hat that fully covers the ears
Hands: cold weather Mittens are warmer than gloves, so mittens are preferred
Feet/Toes: Double pair of socks; an inner moisture-wicking fabric and an outer woolen pair of socks Wear boots that cover the ankles and are water resistant
PRECAUTIONS:
- Tight clothing reduces blood flow and increases the risk of frost bites. Wear dry and loose clothes
- Sweat may conduct heat away from your body. Whenever you feel too warm, take off some of the layers off.
- Wet clothing conducts heat away from the body, so stay dry as often as possible.
- Dehydration increases the risk of frostbite. You may not feel thirsty, so carry bottled water with you when working outside.
- Alcohol, smoking tobacco, cocaine increases your risk for frostbite and hypothermia.
MANAGEMENT
Hypothermia and frostbites Emergencies: seek professional help ASAP.
FIRST AID:
- Get out of the cold weather and move into warm room
- Remove wet clothing to prevent further heat loss
- Keep the victim under dry layers of warm blanket and clothing
- For frostbite, place affected body-parts in lukewarm water
Caution:
- . never use fire dry heat/stove; heating pads, electric blankets to rewarm frostbitten areas.
- . Never put pressure on areas with frostbite: don’t walk on affected feet/toes, do not rub on affected areas. Pressure on the areas with frostbites worsens the injury.




 Lay KPMG audit report on SML-GRA contract before Parliament – Isaac Adongo tells...
Lay KPMG audit report on SML-GRA contract before Parliament – Isaac Adongo tells...
 Supervisor remanded for stabbing businessman with broken bottle and screwdriver
Supervisor remanded for stabbing businessman with broken bottle and screwdriver
 NDC watching EC and NPP closely on Returning Officer recruitment — Omane Boamah
NDC watching EC and NPP closely on Returning Officer recruitment — Omane Boamah
 Your decision to contest for president again is pathetic – Annoh-Dompreh blasts ...
Your decision to contest for president again is pathetic – Annoh-Dompreh blasts ...
 Election 2024: Security agencies ready to keep peace and secure the country — IG...
Election 2024: Security agencies ready to keep peace and secure the country — IG...
 People no longer place value in public basic schools; new uniforms, painting wil...
People no longer place value in public basic schools; new uniforms, painting wil...
 'Comedian' Paul Adom Otchere needs help – Sulemana Braimah
'Comedian' Paul Adom Otchere needs help – Sulemana Braimah
 Ejisu by-election: Only 33% of voters can be swayed by inducement — Global InfoA...
Ejisu by-election: Only 33% of voters can be swayed by inducement — Global InfoA...
 Minority will expose the beneficial owners of SML, recover funds paid to company...
Minority will expose the beneficial owners of SML, recover funds paid to company...
 Prof. Opoku-Agyemang has ‘decapitated’ the NPP’s strategies; don’t take them ser...
Prof. Opoku-Agyemang has ‘decapitated’ the NPP’s strategies; don’t take them ser...
