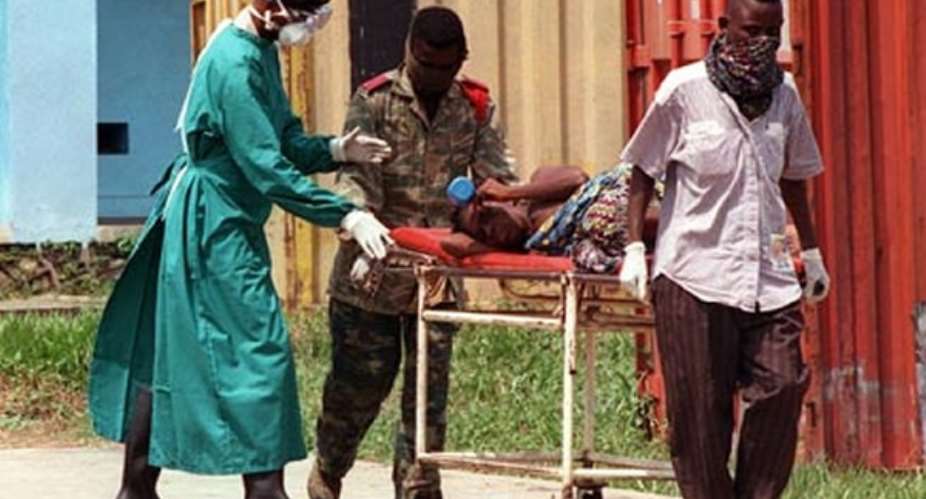
Ghana is heaving a huge sigh of relief after the suspected case of death resulting from Ebola infection was proved negative by the Noguchi Memorial Institute, Monday.
Some Ghanaians were quite apprehensive following reports that a-12-year old girl had died from what was initially suspected to be from an Ebola Virus.
But after samples of blood from the deceased person were analysed, the Noguchi Memorial Institute confirmed the girl did not die from the viral infection.
The news of confirmed Ebola deaths in Guinea and Liberia had alarmed quite a number of people with the Ghana Health Service taking measures to prevent an outbreak of Ebola virus in the country.
The Health Ministry in a statement said "As of 2 April 2014, a total of 134 suspected cases including 84 deaths (case fatality ratio 62.6%) had been reported from 6 districts in Conakry, the capital of Guinea. Forty six (46) clinical samples from Guinea have been confirmed positive for the Ebola virus in the Laboratory analysis. There are possible signs of spread of this deadly disease to other countries.
"The Ministry of Health and Social Welfare (MOHSW) of Liberia has also reported seven (7) suspected cases including three deaths and confirmed two (2)as of 31 March, 2014.
Sierra Leone has identified 2 suspected cases, both of whom died. Both suspected cases reported by Sierra Leone had travelled to Guinea before the onset of the illness.
"Ebola is a severe, infectious often-fatal disease in humans that presents with high fever and bleeding. There is no vaccine against Ebola. It is very infectious and can kill in a short time BUT Ebola can be prevented," the statement said.
Even though the suspected Ebola case in Ghana has been negated, the Health Ministry is admonishing Ghanaians to be on the alert.
"Ebola virus disease is characterized by sudden onset of fever, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, intense weakness, muscle pain, headache and sore throat. This is often followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash, impaired kidney and liver function, and bleeding tendencies (both internal and external) that may include blood spots in the eyes, blood in the vomitus, sputum, urine or stool, bleeding from the nose and other body openings.
Ebola viral disease is spread through the following ways:
Ebola Virus Disease is introduced into the human population through close contact with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected or dead animals.
In Africa, infection has been documented through the handling of infected chimpanzees, gorillas, fruit bats, monkeys, forest antelope and porcupines found dead or ill in the rainforest.
Later Ebola spreads in the community by human-to-human transmission, resulting from close contact with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected people.
Direct physical contact with body fluids of infected persons like blood, saliva, stool, vomitus, urine, and soiled linen.
Burial ceremonies where mourners have direct contact with the body of the deceased person can play a role in the transmission of Ebola.
Measures to be taken to prevent Ebola Virus Disease include the following:
Public education to raise awareness of the risk factors of Ebola infection and the protective measures individuals can take is key to prevent and reduce human infection and deaths as a result. There is no vaccine or medicine for the disease.
Avoid direct contact withfruit bats, chimpanzees, gorillas, monkeys, forest antelope and porcupines found dead or ill in the rainforest.
Avoid direct contact with body fluids of a person suffering from Ebola by using protective materials like gloves, goggles, and masks
Disinfect the beddings and clothing of an infected person with disinfectant
Persons suspected to be suffering from Ebola should be taken to the nearest health unit immediately
People who have died from Ebola should be promptly and safely buried under strict supervision
Persons who have died of Ebola must be handled using appropriate protective wear and buried immediately under strict supervision
Report any suspected cases of Ebola to the nearest health unit immediately
Wash your hands with soap and water after handling a patient or the body of a person who has died of Ebola
Avoid washing of hands from common bowl during funeral rites and other public gatherings
Providing information to people about the nature of the disease, it spreads, and how it can be prevented.
There is no effective treatment and no vaccine,
Steps Taken by Ghana
National Technical Coordinating Committee Meeting to develop comprehensive preparedness and response plans for Ebola
Alert message has been sent to regions, districts and health facilities
Fact Sheet on Ebola, Surveillance and interim Infection Control Recommendations (by WHO) sent to all Regional Directors of Health Services
Port Health staff given orientation on surveillance to detect and notify accordingly
Collaborative surveillance efforts put in place with animal health/Wildlife
Noguchi Memorial Institute of Medical Research has the capacity for laboratory confirmation and are placed on alert to investigate lab samples
Working closely with WHO Country Representative for technical support and advice
Public education / media interaction," the statement concluded.




 Election 2024: Ghanaians will vote to erase Akufo-Addo’s horrifying legacy – Nii...
Election 2024: Ghanaians will vote to erase Akufo-Addo’s horrifying legacy – Nii...
 BP killed ex-Weija-Gbawe MCE – Tina Mensah reveals
BP killed ex-Weija-Gbawe MCE – Tina Mensah reveals
 Limited voter registration exercise: NDC slams EC over mass technical challenges
Limited voter registration exercise: NDC slams EC over mass technical challenges
 UK, America will one day come to Ghana to borrow Akufo-Addo to be their presiden...
UK, America will one day come to Ghana to borrow Akufo-Addo to be their presiden...
 EOCO returns fire at OSP over Cecilia Abena Dapaah’s money laundering case
EOCO returns fire at OSP over Cecilia Abena Dapaah’s money laundering case
 Anti-corruption endeavours must be rooted in systems, investigations and prosecu...
Anti-corruption endeavours must be rooted in systems, investigations and prosecu...
 We’ve not introduced 1% cybersecurity levy on banking transactions – BoG
We’ve not introduced 1% cybersecurity levy on banking transactions – BoG
 EU hits out at sidelining of Chad election observers
EU hits out at sidelining of Chad election observers
 ‘Be calm; we’re having engagements on new fee implementation’ — KNUST SRC assure...
‘Be calm; we’re having engagements on new fee implementation’ — KNUST SRC assure...
 Bawumia is compassionate, unique politician without corruption tag — Miracles Ab...
Bawumia is compassionate, unique politician without corruption tag — Miracles Ab...
