Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids (Piles) are engorged veins in the lower parts of the rectum, and Anus.
Piles are usually, caused by pressure build up in the veins of the anus and lower rectum.
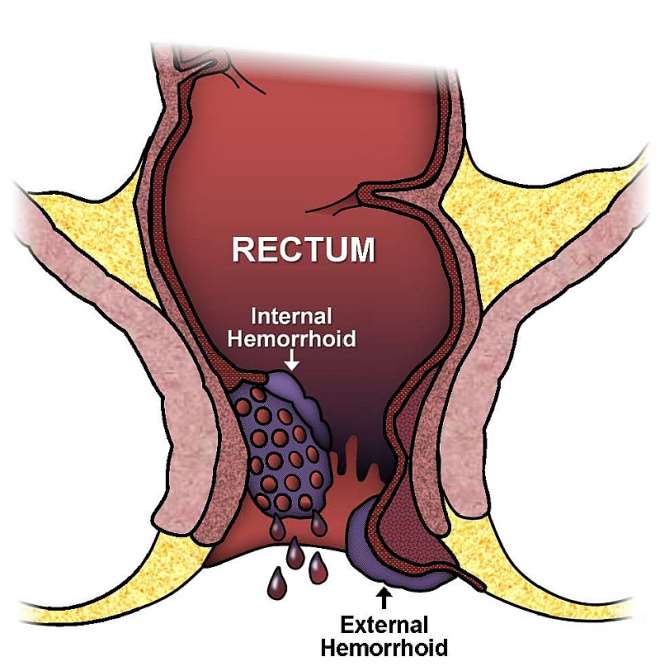
Piles that develop in the lower rectum and upper parts of the anus are known as Internal hemorrhoids; they are covered by normal gut lining and are therefore painless.
Piles that develop beneath the skin around the anus are known as External hemorrhoids. External hemorrhoids are covered by normal skin so they could become painful and itchy.
Piles may cause problems when the swollen veins bleed, when blood clot forms in the swollen veins, or when the swollen vein prolapse into the anal canal or outside and gets its blood supply, compromised.
Behaviors that increase venous pressure in the lower rectum include:
. Chronic Constipation (Hard stool, straining at stool)
. Pregnancy
, A sedentary lifestyle.
. Obesity
. Excessive sitting on the toilet to read or chat on social media.
. Frequent lifting of heavy weights.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Bleeding. Blood may be found on the stool or on the tissue wipes. If bleeding is severe enough, the affected person could develop anemia
Hemorrhoidal Pain may be due to either blood clots formation in the external hemorrhoid, or the loss of arteria blood supply to a prolapsed internal hemorrhoid.
The pain may be sudden and intense, it lasts for several days, and then gets better.
The hemorrhoid may protrude during bowel movements.
Anal itch
Sensitive lump(s) in the anal region
COMPLICATION OF HEMORRHOIDS:
. Bleeding. Hemorrhoids may bleed. Usually blood is found on the tissue wipes. Persistent bleeding could lead to severe anemia
. Prolapse, the hemorrhoid may stick out into the anal lumen, and protrude outside
. Thrombus formation; Blood Clot may form in the piles. This makes the hemorrhoid hard and painful. Thrombosed hemorrhoids appear as tense, painful bluish lumps at the anus.
. Strangulated hemorrhoids (a prolapsed Internal hemorrhoid gets tightly squeezed by the anal sphincter muscles. This, may compromise its blood supply). The piles become very painful and incapacitating.
PREVENTION OF HEMORRHOIDS
. Drink more (Liberal) fluids. Your urine color may indicate if you are drinking enough water. Slight yellow to colorless urine is preferred.
. Consume a High fiber diet that promotes bulky stool formation. Include Banana, Pawpaw and other fruits, vegetables and whole grains in your diet.
If you are not a fan of Fruits and Vegetables, you could add Fiber Supplements to your diet. A minimum of 25-30 g of fiber a day is preferred.
PROBLEMS THAT COULD BE MISTAKEN FOR PILES
Bleeding from the anus could be due to other diseases of the anus, rectum and the colon.
What you suspect as hemorrhoids could be a different mass like Anal Cancer or Anal Fissure.
Rectal prolapse and rectal polys could be mistaken for hemorrhoids.
These are the reasons you may need to see a doctor first, prior to self-treatment
EVALUATION OF PILES.
Physicians use an Anoscope, to view the lumen of the anus and examine the internal hemorrhoids.
They may use a sigmoidoscope or colonoscope to look for and exclude tumors and diseases of the sigmoid colon.
MANAGEMENT OF PILES
The first step for controlling hemorrhoids is Dietary modification.
When you increase your oral fiber intake (greater than 30g/d) you avoid (and cure) Constipation and Straining at stool.
You may need to add Psyllium seeds (Metamucil), Methylcellulose (Citrucel) to your diet, as fiber supplements.
. Adequate oral fluid intake, greater than 1-1.5 liters of fluid helps avoid hard stool formation and straining.
Straining engorges the hemorrhoids. Decreasing straining and constipation decreases the size of hemorrhoids.
. Avoid prolonged toilet sitting (it engorges the hemorrhoids).
EXTERNAL HEMORRHOIDS
An External hemorrhoid requires no specific treatment unless it becomes acutely thrombosed or causes pain and discomfort.
Warm bathtubs for about 20 minutes, 2-3 times a day. Bathing in tubs with warm water eases painful hemorrhoids.
For pain and discomfort: Anti-inflammatory Suppositories and soothing topical Creams including hydrocortisone, may be applied.
INTERNAL HEMORRHOIDS
For strangulated hemorrhoids, treatment include Bed rest, Hot tub baths, and Ice packs. Topical Nifedipine 0.3% Creams (to relax the sphincters) and Pain medications.
Mild and moderate cases of bleeding Internal hemorrhoids are treated Non-operatively.
Non-operative approaches include: the use of rubber band to ligate the hemorrhoid at its base.
The band causes the hemorrhoid to shrink.
Blood-clotting Chemicals may be injected into Bleeding hemorrhoids that are not protruding to stop the bleed.
SURGERY
Surgery is reserved for cases that don’t resolve or improve with lifestyle modifications and non-surgical methods.
Physicians may tie off the artery that feeds the hemorrhoid (hemorrhoidal artery).
Physicians may use circular staples to hook the hemorrhoids back into their normal position
Thrombosed hemorrhoids may require surgical evacuation if seen in the first 2 days.
Other piles that cause pain, discomfort, and severe blood loss are usually removed surgically, after a trial of non-surgical methods.
ALEX SARKODIE MD.





 SSNIT must be managed without gov’t interference – Austin Gamey
SSNIT must be managed without gov’t interference – Austin Gamey
 Ejisu by-election could go either way between NPP and independent candidate — Gl...
Ejisu by-election could go either way between NPP and independent candidate — Gl...
 We never asked ministers, DCEs to bring NPP apparatchiks for returning officer r...
We never asked ministers, DCEs to bring NPP apparatchiks for returning officer r...
 No one denigrated the commission when you appointed NDC sympathizers during your...
No one denigrated the commission when you appointed NDC sympathizers during your...
 Used cloth dealers protests over delayed Kumasi Central Market project
Used cloth dealers protests over delayed Kumasi Central Market project
 A/R: Kwadaso onion market traders refuse to relocate to new site
A/R: Kwadaso onion market traders refuse to relocate to new site
 Dumsor: Corn mill operators at Kaneshie market face financial crisis
Dumsor: Corn mill operators at Kaneshie market face financial crisis
 Jamestown fishermen seek support over destruction of canoes by Tuesday's heavy d...
Jamestown fishermen seek support over destruction of canoes by Tuesday's heavy d...
 Election 2024: EC to commence voter registration exercise on May 7
Election 2024: EC to commence voter registration exercise on May 7
 Public schools rebranding: We’re switching to blue and white, we’re painting all...
Public schools rebranding: We’re switching to blue and white, we’re painting all...
