VITAMIN D, THE SUNSHINE VITAMIN
Vitamin D, the only vitamin that acts as a hormone, has receptors (VDR) in every tissue in the body.
VDR have been found in the brain, heart, muscles, lungs, and also in the immune system.
For the body to function properly, vitamin D must be present and in adequate quantities.
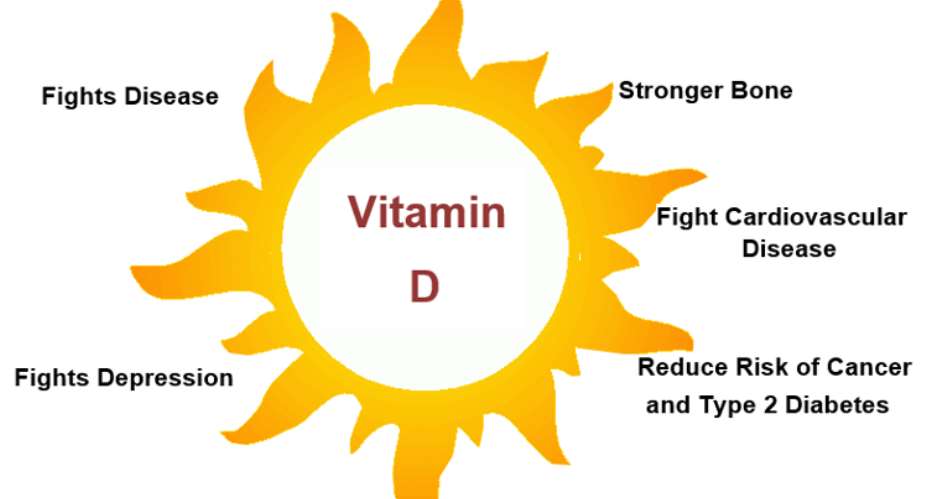
Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with many diseases.
Disease State associated with Low Vitamin D levels
. Vitamin D is crucial for bone and muscle strength. Low levels lead to Osteoporosis, fractures and falls
. Vitamin D promotes free flow of blood in the tiny blood vessels. A lack of Vitamin D leads to circulation problems, including: Peripheral artery disease, Coronary artery disease, Erectile dysfunction, Heart failure
. Vitamin D decreases inflammation, and its deficiency has been associated with increase asthma exacerbation and severity.
. Low vitamin D levels have been associated with Cognitive impairment, including poor executive functions, dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
. High Vitamin D status provides protection against Parkinson's disease.
. Infections including: Bacterial vaginosis and viral influenza have been associated with low vitamin D levels.
. Low vitamin D levels have been associated with diabetes, hypertension, obesity, dyslipidemia all of which are risk factors for Metabolic syndrome
. Vitamin D modulates the immune system. Calcitriol supplementation decreases the incidence and severity of Autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis
BIOSYNTHESIS OF VITAMIN D:
Vitamin D is photosynthesized (with UV-B sunlight, 290-330 nm) in both plants and animal.
Vitamin D formed by sunlight in plants is known as Vitamin D2, or ergocalciferol.
Vitamin D formed by sunlight in the skins of animals is known as Vitamin D3 or cholecalciferol.
VITAMIN D METABOLIC PATHWAYS.
Ultraviolet radiation from the sun (290-330nm) convert 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin to cholecalciferol (vitamin D3). (Ergocalciferol, vitamin D2 is formed in plants)
Vitamin D3 undergoes a series of hydroxylation processes to become an active hormone.
Hydroxylation of vitamin D, first occurs in the liver to yield 25(OH)D3 also known as Calcidiol.
The next hydroxylation step occurs in the kidneys to yield the active form of vitamin D: 1,25(OH)2 D3 also called Calcitriol.
Calcitriol has biological actions, including activation of cells to secret proteins and other chemicals, when it binds to the various vitamin D receptors (VDR) on these cells.
ASSESSMENT OF VITAMIN D LEVELS.
A low serum level of 25(OH)D, the principal form of circulating vitamin D, is the main marker of vitamin D deficiency.
The half-life of 25(OH)D is about 15 days.
Vitamin D status:
Deficiency: 20ng/ml (50nmol/L)
Insufficiency 21-29ng/ml
Sufficiency >30ng/ml [1]
Potentially harmful: > 150ngml
There is a low level 25(OH)Vitamin D in the populations from developing countries even in sunny climates [2]
RISK FACTORS FOR VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY
. Body Mass Index greater than 30. Excessive fat dilutes the vitamin D concentration in the body.
. Ageing and the aged: Old skin are less efficient in vitamin D photosynthesis.
. Inadequate exposure to sunlight.
. Kidney and Liver diseases. (N.B Active vitamin D is produced in these organs)
. Naturally dark skin tone
. Smoking
. Using sunscreen creams and lotions
. Wearing sunscreen clothes.
Dark-skinned individuals have high level of melanin which acts as a sunscreen to impair vitamin D photosynthesis.
In north America and Europe, and other temperate countries vitamin D deficiency is more common in blacks than in Caucasians.
African Immigrants in temperate climates, need to monitor their vitamin D levels annually.
The use of sunscreens completely blocks photosynthesis of vitamin D and reduces circulating vitamin D levels.
Humans obtain vitamin D from 3 sources:
. UV-B sunlight exposure
. Diet
. Vitamin D3 supplements.
The only way to know if one has adequate vitamin D level, is to measure 25(OH)D blood concentration.
Epidemiological studies suggest vitamin D deficiency may be a significant risk factor for many diseases.
What are the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of vitamin D. 1microgram vitamin D is equal to 40 international units (IU)
Assuming minimal sun exposure (1)
Age 1-70 years:15 micrograms per day (600 IU per day)
Age 71 and over: 20 micrograms per day (800 IU per day)
Include naturally vitamin-D-rich foods, example fatty fish such as salmon, trout, sword fish and tuna, eggs, mushroom in your diet,
VITAMIN D AND CANCER PREVENTION.
Numerous studies in laboratories and in animals, as well as observation in human populations, have shown that calcitriol 1,25(OH)2 D, possesses antineoplastic activity.
Compared with subjects who had the lowest vitamin D levels, those with a high vitamin D levels had a 20% lower risk of cancer overall
Calcitriol, 1,25-dihydrovitamin D, affect gene expression by activating the vitamin D receptors (VDRs)
Preclinical studies show 1,25(OH)2D3 and its analogs have anti-tumor effects in vivo and in vitro, (2) through multiple mechanisms including:
. slow cancer cell growth,
. stimulate cancerous cell death and
. Starve cancer cells of their blood supply (angiogenesis)
. Inhibit spread of cancer cells.
. Potentiates the effect of other anti-cancer agents.
The findings support the application of 1,25(OH)D3 in cancer prevention and treatment (2)
Among the cancers that have been associated with low vitamin D levels and improvement with vitamin D supplementation include:
. Colorectal cancers (3)
. Breast cancers (4)
. Prostate cancer (5)
. Ovarian cancers (6)(7)
. Pancreatic cancer and other diseases of the pancreas (8)
Vitamin D reduces the risk of many types of cancer. However, since no specific randomized controlled trials have been successfully conducted, instead of these observational and ecological studies, vitamin D and its metabolites are not being recommended as part of cancer prevention and treatment. Researches to this effect are still, ongoing.
VITAMIN D AND DIABETES
Vitamin D activates Vitamin D receptors that speed up the production of proteins which protect pancreatic beta cells from stress. The beta cells of the pancreas produce insulin. Vitamin D improves insulin sensitivity.
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with islet beta cell function, insulin resistance and diabetes.
VITAMIN D AND IMMUNITY
Vitamin D modulates the immune system.
Immune cells: macrophages, monocytes, lymphocytes, have vitamin D receptors on their cell membranes. Vitamin D enters these cells, leading to the production of anti-inflammatory and pro-immune proteins. These proteins inhibit inflammatory reactions and prevent autoimmune diseases (9)
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHROMATOSIS
Administration of vitamin D 2,000 IU daily or 5,000 IU weekly has been found to reduce disease activity and improve of fatigue and other symptoms of SLE. (10)
PREVENTION OF TYPE ONE DIABETES
Regular doses of vitamin D 2000 IU/day in early life has been shown to decrease the risk of developing type1 diabetes (up to 80% reduction projected over the next 30 years (11)
VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY AD MENTAL ILLNESS
Studies have indicated that vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency are both highly prevalent in adolescents with severe mental illness, especially in the black population. (12)
During the winter periods, there is an increase in the incidence of persons with the type of depression, known as seasonal affective disorder (SAD). SAD may be due to changing levels of vitamin D3, which may affect serotonin levels in the brain
VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY AND IMPOTENCE
Blood vessels in the penis, dilate for the penis to become turgid. Vitamin D helps in opening up of small blood vessels to allow the free flow of blood. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with greater prevalence of erectile dysfunction
HOW TO IMPROVE VITAMIN D STATUS
4 ways to improve vitamin D levels
Exercise, sunlight exposure, consuming vitamin-rich foods and taking vitamin D supplements.
EXERCISE
Both indoor and outdoor exercises improve vitamin D levels
EXPOSURE TO SUNLIGHT
Just 15 minutes of sunlight in the tropics, or in summer produces about 3000 IU of vitamin D, depending on your skin pigmentation and latitude.
DURATION OF OUTDOOR ACTIVITIES.
. Light skin: 15-20 minutes
. Medium skin: 25-30 minutes
. Dark skin: 40-45 minutes
Vitamin D skin production is influenced by:
Age: Those in their 20's produce 4 times as much cholecalciferol as people aged 65 years and over.
Skin color: Whites produce twice as much cholecalciferol as blacks, due to heavy melanin pigmentation.
DIETARY SOURCES OF VITAMIN D
There aren't many Vitamin D rich foods
Food Vitamin D (IU)
Salmon, 3.5 ounces 360
Mackerel 3.5 ounces 345
Tuna, canned, 3.5 ounces 200
Fortified milk 8 ounces 98
VITAMIN D SUPPLEMENTS
Supplements are the best way to ensure, one gets the daily 600-800 IU per day of vitamin D3, in the absence of adequate sunlight exposure. Higher doses are prescribed for those with vitamin D deficiency
Most multivitamins contain 400IU of vitamin D, together with other vitamins. It may be unsafe to take 2 tablets of these vitamins, since this doubles the doses of the other minerals and vitamins in the tablet.
Take only vitamin D specific vitamins, not the non-specific multivitamins.
Currently, it is safe to take up to 2000 IU vitamin D3 per day. Mega doses of vitamin D are of unproven benefits.
References:
-
Institute of medicine committee to review dietary reference intakes for vitamin D and calcium. Dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2011.
-
Jeffery LE, Qureshi OS, Gardner D, et al (2015) Vitamin D Antagonizes the suppressive Effect of inflammatory Cytokines on CTLA-4 expression and Regulatory Function. PLoS one, 10: E0131539
-
Abou-Rays; Helmil M: The effect of vitamin D supplementation on inflammatory and hemostatic markers and disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythromatoses : a randomized placebo control trial. J rheumatol (2013) 40(3) 265-72.10.3899/jrheum111594
-
Intake of vitamin D and risk of type 1 diabetes; a birth control-cohort study. Lancet 2001, 358(9292); 1500-3 [Pubmed]




 SSNIT must be managed without gov’t interference – Austin Gamey
SSNIT must be managed without gov’t interference – Austin Gamey
 Ejisu by-election could go either way between NPP and independent candidate — Gl...
Ejisu by-election could go either way between NPP and independent candidate — Gl...
 We never asked ministers, DCEs to bring NPP apparatchiks for returning officer r...
We never asked ministers, DCEs to bring NPP apparatchiks for returning officer r...
 No one denigrated the commission when you appointed NDC sympathizers during your...
No one denigrated the commission when you appointed NDC sympathizers during your...
 Used cloth dealers protests over delayed Kumasi Central Market project
Used cloth dealers protests over delayed Kumasi Central Market project
 A/R: Kwadaso onion market traders refuse to relocate to new site
A/R: Kwadaso onion market traders refuse to relocate to new site
 Dumsor: Corn mill operators at Kaneshie market face financial crisis
Dumsor: Corn mill operators at Kaneshie market face financial crisis
 Jamestown fishermen seek support over destruction of canoes by Tuesday's heavy d...
Jamestown fishermen seek support over destruction of canoes by Tuesday's heavy d...
 Election 2024: EC to commence voter registration exercise on May 7
Election 2024: EC to commence voter registration exercise on May 7
 Public schools rebranding: We’re switching to blue and white, we’re painting all...
Public schools rebranding: We’re switching to blue and white, we’re painting all...
