CONSTIPATION
Worldwide, about 12% of the population suffer from constipation.
Constipation is more common in
. Women (female-male-ratio is 3:1)
. Pregnancy
What is constipation?
Constipation is a symptom, rather than a disease
A person having any 2 or more of the following symptoms in the preceding 3 months, has constipation:
. Infrequent defecation, less than 3 bowel movement per week
. Straining at defecation
. Passage of hard or lumpy stool
. Sensation of incomplete defecation
. Sensation of obstruction in the anus
. Passage of toilet-clogging stools.
. Use of laxatives and manual methods to promote defecation.
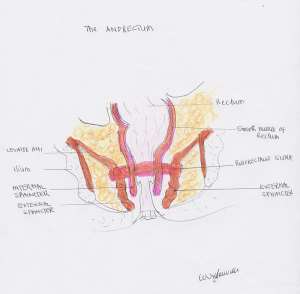
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
Ingested food is digested and absorbed from the small intestine.
The colon absorbs water from the small intestinal effluence. The longer the colon transit time, the harder the effluence gets, as more and more water is absorbed by the colon.
The internal anal sphincter relaxes to allow stool pass into the anal canal.
The external anal sphincter voluntarily contracts to stop defecation (and relaxes to allow defecation).
Defecation occurs when the pelvic floor muscles (puborectalis sling and the external anal sphincter) relax synchronously, for stool elimination.
Failure of these muscles to relax during defecation, (a condition called Pelvis floor dyssynergia), leads to constipation.
COMPLAINTS
A person with constipation, may have no complaints, or may complain of
. Bloating
. Low back pain
. Rectal bleeding
. Pain on defecation
. Diarrhea or fecal soiling
What causes Constipation?
Primary(innate) and Secondary(modifiable) causes
Primary causes:
. Pelvis Floor Dyssynergia:
The pelvis floor muscles fail to relax during defecation.
Patients strain at stooling and they may have the feeling of incomplete bowel motion. They may, at times, use their fingers to bring out the feces.
It is a behavioral disorder that may occur after sexual abuse, pelvis trauma or pelvis surgery
. Slow transit constipation: This is common in young women.
The movement of fecal stream in the colon is much slower.
Affected persons have infrequent bowel motion, decreased urged to defecate and may strain at stool.
. Sensory Abnormality in the rectum, that lead to decreased urge to defecate. The person may be unaware of their need to defecate. This is common in children.
Secondary causes
Usually multifactorial. Constipation is a symptom with many etiologies.
The etiology may include diet, personal lifestyle and behaviors that promote constipation:
. Inadequate fluids intake.
. Inadequate Fiber intake
. Reduced levels of exercise.
Other causes include medications, especially opioid analgesics like codeine
Medications:
NSAIDs: naproxen, ibuprofen.
Narcotic analgesics: codeine
BP medications: Beta- and the calcium channel blockers, Diuretics
Antidiarrheal agents: imodium
Neuro-muscular pathologies
Parkinson disease, Multiple sclerosis, Spinal cord lesions, Hirschsprung disease, Cerebral palsy
Metabolic
. Pregnancy
. Diabetes
. Hypothyroidism
. Low Potassium
. High serum calcium levels
Mechanical
Colon cancer, blocks effluent flow
Pelvic tumors
Anal stenosis/strictures/Fissures
In the older adult population, constipation may be a sign of colorectal cancer or other pathologies and requires urgent evaluation.
The red flags include:
Age :>45 years
New-onset constipation in the elderly
Rectal bleeding
Unexplained weight loss
Inability to pass flatus
Family history of colon cancer
History of abdominal cancers and radiation therapy
COMPLICATIONS OF CONSTIPATION
. Hemorrhoids: results for straining at stools
. Anal fissure: painful tears at the anus, due to hard stools. Fissures may bleed and cause burning pain on defecating
. Rectal prolapse, especially in children
. Bowel obstruction
. Urinary retention and bladder infections
. Diverticular disease of the colon
PREVENTION
Lifestyle modification.
-
Increase physical activity, exercise regularly.
-
Drink plenty of fluids
-
Increase fiber intake.: up to 14 grams of fiber for every 1000calories in the diet. The natural way to increase fiber intake: eat more fruits and vegetables daily, and consume whole grains, legumes, beans regularly.
-
Don't ignore the urge to have a bowel movement
Stool Softeners: (in the elderly population) lower stools surface tension, enabling stools to absorb more water and become softer. Docusate soften stools by allowing water and fat into the stools.
Docusate sodium 50-300mg once daily, oral. (The dose for Docusate calcium is 240mg orally, once a day)
TREATMENT OF CONSTIPATION
Chronic Constipation
A plain abdominal X-ray may indicate the presence of fecal material in the large intestine. For such persons, the first step is:
Fecal Disimpaction.
Disimpaction may be achieved manually and/or with
-
Enema: Mineral oil: Fleet mineral oil is a lubricant lexative1 bottle (4oz) rectally as single dose. or
2. Orally with Polyethylene glycol (PEG) 17g in 4oz water orally, every 15 minutes until the patient has a bowel motion, or until 8 glasses have been consumed.
In children the dose for fecal disimpaction, is 1.5g/Kg daily for 3 days.
Once fecal disimpaction has been achieved, affected persons need to be placed on maintenance anti-constipation mediations.
Constipation medications
(a). Bulk-forming agents: Great for long-term treatment of constipation.
. Psyllium (Metamucil) 5 grams with meals, 2-3 times daily. The recommendation is to start psyllium at 5gram doses three times a day.
. Methylcellulose(Citrucel) 500mg caplets. Take 2 caplets 4-6 times/day.
(b). Osmotic Laxatives: they draw water from gut wall into the lumen of the gut to soften and make stools easier to pass. It may take 2-3 days before improvement is noticed
. Lactulose: 10g/15ml. Take 15-30ml orally once daily, and up to three or four times daily
. Sorbitol: oral 30-150ml (70%solution) once
. Polyethylene Glycol(PEG)3350.: 17g in 4-8oz water orally, once daily for 3-6 days.
(c.) Stimulant laxatives: Stimulate the smooth intestinal muscle to speed up bowel movement.
Stimulants are fast-acting, within 8-12 hours.
Great for Slow-transit constipations and acute exacerbation of constipations.
Stimulants are used for short term only.
. Senna (SENOKOT 15mg: Take 2 tablets orally once or twice a day). Chronic use darkens the lining of the colon: melanosis coli.
. Bisacodyl (Dulcolax) take 1 to 3 tablets in a single daily dose.
Pelvis floor dyssynergia:
For those with Dyssynergia: Physical therapy with biofeedback helps.
Alex Sarkodie, MD




 SSNIT must be managed without gov’t interference – Austin Gamey
SSNIT must be managed without gov’t interference – Austin Gamey
 Ejisu by-election could go either way between NPP and independent candidate — Gl...
Ejisu by-election could go either way between NPP and independent candidate — Gl...
 We never asked ministers, DCEs to bring NPP apparatchiks for returning officer r...
We never asked ministers, DCEs to bring NPP apparatchiks for returning officer r...
 No one denigrated the commission when you appointed NDC sympathizers during your...
No one denigrated the commission when you appointed NDC sympathizers during your...
 Used cloth dealers protests over delayed Kumasi Central Market project
Used cloth dealers protests over delayed Kumasi Central Market project
 A/R: Kwadaso onion market traders refuse to relocate to new site
A/R: Kwadaso onion market traders refuse to relocate to new site
 Dumsor: Corn mill operators at Kaneshie market face financial crisis
Dumsor: Corn mill operators at Kaneshie market face financial crisis
 Jamestown fishermen seek support over destruction of canoes by Tuesday's heavy d...
Jamestown fishermen seek support over destruction of canoes by Tuesday's heavy d...
 Election 2024: EC to commence voter registration exercise on May 7
Election 2024: EC to commence voter registration exercise on May 7
 Public schools rebranding: We’re switching to blue and white, we’re painting all...
Public schools rebranding: We’re switching to blue and white, we’re painting all...
