BEDWETTING (Nocturnal Enuresis)
Bladder control & Epidemiology
Most children are able to control their bladder, during sleep, by the age of five years. However, 1:5 five-year old kids, wet their beds at night; 1:10 five-year old kids wet themselves during the day, at least once every 2 weeks. By the age of 10 years less than 1:20 kids wet their bed at night. Daytime wetting is more frequent in girls; night time bedwetting is more common among boys.
About 2 % of teens, wet their beds during sleep.
About 1-2 % of Adults wet their beds at night
Bedwetting is most common in children, and in some Stressed Adults too.
Definition
When a person, older than 5 years, voids urine in bed or on their clothes, at least twice in a week, for 3 consecutive months, they are said to be bed-wetting
There are two types of bed-wetting: Primary (child has never had a period of dryness since birth) and Secondary in which the child has had 3 months of sustained dryness during daytime, and 6 months of bedtime dryness.
Causes
a.) Heredity: Bed-wetting tends to run in families. If both parents used to wet their beds, 3:4 of their children, shall have bedwetting issues; if only one parent had the bedwetting history, 2:5 of their kids shall wet their beds during sleep. Apart from genetic predispositions, there may be other medical causes. The list could be long
. Bladder dysfunction: Overactive Bladder (bladder frequently contracts to expels urine, even if not distended)
. Increased urine production at bedtime
. Persons who Fall into deep sleep, and are difficult to arouse from their sleep
. Persons with Sleep Apnea tend wet their beds
. Those with Anatomical problems in their urinary tract (ectopic ureter)
. Emotional Stressful situations
. Sickle Cell Kidney disease
. Constipation (bulky stools in the rectum decreases bladder volumes)
EVALUATION
URINE ANALYSIS: Urine examination is the first step in evaluating for nocturnal enuresis
. Presence of WBCs and Bacteria in the urine, predicts bladder and urinary tract infections.
. Presence of RBCs and proteins in the urine predicts Kidney diseases
. Urine with low specific gravity predicts diabetes insipidus (inability to concentrate urine) or the person intentionally, drinks too much water
TREATMENT
Most kids 5 years and younger stop their bed-wetting on their own and they therefore, require no treatments.
Treatment is available for those who are 6 years and older.
Successful treatment requires a well-motivated child and a Cooperative and Supportive Family.
- Conservative measures. These include
. Decreasing fluid intake several hours before bedtime
. Child Voids urine just before they go to bed, and just before the parents go to bed
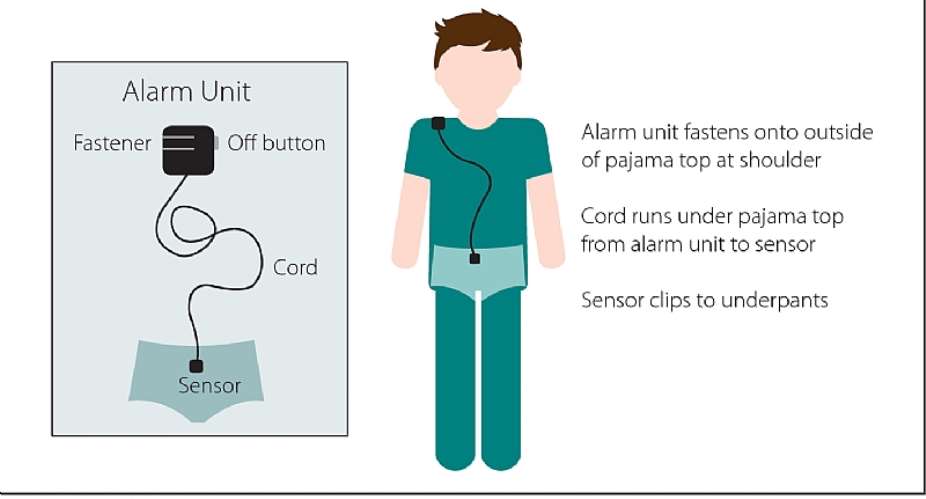
- Bed-wetting Alarms
The child wears a moisture sensor in their underwear/pajamas. The sensor triggers an audible alarm when it senses urine in the underwear/pajamas. The alarm wakes the child up. When used consistently, bed-wetting alarms are the most effective interventions against bed-wetting. Typically, the alarm is worn at bedtime for 2-3 months or until the child stays dry for 2 continuous weeks.
- Medications
. Desmopressin (DDVAP). Desmopressin is the most often used medication for bed-wetting. It helps the kidneys to reabsorb more water, and thus reduce the volume of urine production. It is given at bedtime. It may take 2-3 months to see results.
. Oxybutynin: Relaxes the bladder muscles and therefore useful for those with overactive bladders.
A combination of conservative measures, Bed-wetting alarms and medications often solve bed-wetting problems.
Those who do not show improvement, despite adhering to treatment recommendations could be referred to Bladder, and /or Kidney Physicians.




 This IMANI job no dey pap; the people you are fighting for are always fighting y...
This IMANI job no dey pap; the people you are fighting for are always fighting y...
 Prof. Naana Opoku-Agyemang has changed; you can see a certain sense of urgency –...
Prof. Naana Opoku-Agyemang has changed; you can see a certain sense of urgency –...
 MFWA Executive Director slams Akoma FM for engaging in ‘irresponsible’ media pra...
MFWA Executive Director slams Akoma FM for engaging in ‘irresponsible’ media pra...
 ‘Women must become millionaires too’ — Prof Jane Naana on establishment of Women...
‘Women must become millionaires too’ — Prof Jane Naana on establishment of Women...
 Some believe only in Ghanaian votes, not Ghana — Kofi Asare jabs politicians
Some believe only in Ghanaian votes, not Ghana — Kofi Asare jabs politicians
 Plan to make BEST sole aggregator of Sentuo Oil Refinery will create market chal...
Plan to make BEST sole aggregator of Sentuo Oil Refinery will create market chal...
 2024 elections: I can't have the man I removed from office as my successor — Aku...
2024 elections: I can't have the man I removed from office as my successor — Aku...
 2024 Elections: Immediate-past NPP Germany Branch Chairman garners massive votes...
2024 Elections: Immediate-past NPP Germany Branch Chairman garners massive votes...
 Gov’t focused on making Ghana energy self-sufficient, eco-friendly – Akufo-Addo
Gov’t focused on making Ghana energy self-sufficient, eco-friendly – Akufo-Addo
 April 25: Cedi sells at GHS13.74 to $1, GHS13.14 on BoG interbank
April 25: Cedi sells at GHS13.74 to $1, GHS13.14 on BoG interbank
