Zinc deficiency affects over two billion people, in the developing countries and according to the WHO, Zinc deficiency is the fifth leading cause of mortality and morbidity in developing countries.
Worldwide, zinc deficiency accounts for 16% of lung infections, 18% of malaria and 10% of Diarrheal diseases.
Zinc deficiency in children leads to stunted growth. In the Elderly, Zinc deficiency may lead to serious infections, and in the male adult, Zinc deficiency may lead to Impotence and loss of Zinc protection from Prostate malignancies.
MICRONUTRIENTS.
Micronutrients are nutrients required by the body, not as a source of energy, for cellular metabolism and enzyme activities and protection of the body against oxidative damages. They include iron, zinc, iodine, Vitamins A, B, C, and D. Zinc is the most abundant mineral, after iron, in the body.
Zinc is an essential micronutrient for human health, all human beings need Zinc for survival.
Zinc is well distributed and found in all body tissues and fluids. However, Zinc has no specialized storage systems in the body. This means, Zinc must be ingested regularly to maintain a steady state.
Ensuring adequate zinc intake, is important in decreasing illnesses, promoting physical growth and reducing mortality.
ZINC METABOLISM.
Zinc is absorbed throughout the small intestines. Absorption is better with liquid diets, than with solid diets.
Zinc is eliminated from the body thorough Kidneys (urine), Intestines (feces) Skin (sweat). Strenuous exercises and hot weather promote Zinc losses through perspiration.
ROLE OF ZINC IN HUMAN HEALTH
Zinc is an essential micronutrient. Humans require zinc for survival.
. Many enzymes in the body need zinc to function properly.
. Zinc acts as cofactor for enzymes involved in Protein, carbohydrate, Lipid and DNA/RNA metabolism.
. Zinc Plays a role in the transcription of genetic codes and genetic expressions.
Zinc modulates inflammatory reactions by targeting Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-kB), a transcription factor that is a master regulator of inflammatory responses. Zinc is involved in regulating inflammatory cytokines like Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and IL-1B.
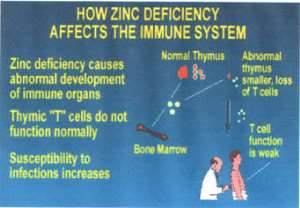
. Zinc plays a role in immune function, it affects with production of Antibodies and T-cells (both cellular and humoral immunity) which help to fight infections and certain forms of cancers. T-cells help the body fight against fungal, TB and certain viral infections, and destroy cancer cells. Zinc deficiency leads to worse outcome in response towards bacterial infections and sepsis.
. Zinc promotes Normal Growth by promoting Growth hormone and Somatomedin-C production and secretions. (Somatomedin-C activates bone-cartilage) Zinc also interacts with Testosterone, Thyroxine, Insulin and Vitamin D3, to promote bone growth. Zinc deficiency leads to impaired weight to height relationship, leading to Stunted Growth. About a third of the world’s population, has stunted growth, due to zinc deficiency.
. Zinc is required for smell and taste acuity and a deficiency leads to appetite loss and taste abnormalities. These lead to a low desire to eat.
Zinc plays a critical role in many biological pathways and physiological processes in the body including: Cell growth, Cell differentiation and metabolism
. Zinc helps in testosterone production, and low zinc levels may be a factor in erectile dysfunction.
Zinc acts as antioxidant, it stabilizes Cell membranes and cell molecules, (from oxidations and injuries by free radicals) by reducing free radicals and preventing lipid peroxidation.
For Zinc to perform these actions, its homeostasis is critical.
Zinc deficiency is related to inadequate zinc intake, Poor dietary Zinc absorption from the small intestines and loss from diarrheal illnesses
POPULATIONS AT RISK FOR ZINC DEFICIENCY:
. Malnutrition, (including Kwashiorkor, Marasmus.)
. Pregnancy, during the 3rd trimester, zinc requirements is twice that of the non-pregnant female.
. Lactation period where zinc is channeled for breast milk production.
. Elderly population, due to poor intestinal zinc absorption.
, Vegetarians, most plants have low levels of zinc, and also lower bioavailability due to high amount of phytic acid. Soaking Beans, grains and seeds in water for about 6 hours before cooking, and allowing them to sit after cooking until sprout forms, help reduce the phytate content in those foods.
Sickle cell disease: 44% of kids with SCD, 65% of adults with SCD have Zinc deficiency
. Alcoholics: Alcohol consumption reduces intestinal absorption of zinc, and increase renal elimination of zinc. About half of alcoholics have zinc deficiency.
. People with Bowel abnormalities: short bowel syndrome, Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
. Athletes who perspire a lot
NORMAL SERUM ZINC LEVEL
A simple blood sample may be used to assess current zinc level in the serum.
Reference values: Normal serum zinc is 0.66 to 1.10 mcg/mL
MANIFESTATIONS, ZINC DEFICIENCY
. Growth retardation/ Stunted growth
. Loss of appetite
. Impaired immune function leading to decreased resistant to infections and certain cancers.
Severe Zinc deficiency is characterized by:
. Hair loss
. Diarrhea
. Delayed sexual maturation
. Impotence and hypogonadism in males.
. Delayed wound healing and Skin Rashes
. Decreased appetite and Taste abnormalities
. Mental lethargy
. Recurrent Pneumonia, Diarrhea, Malaria and other infections.
Many of the symptoms are not specific to Zinc deficiency, since these symptoms are often associated with other health conditions. Zinc level may be assessed to determine deficiency.
NATURAL SOURCES OF ZINC.
. Lean red Meat, including beef and pork.
. Oysters, Crabs and Lobster are also high sources of Zinc.
. Whole grain cereals (milling decrease zinc concentration).
. Legumes.
However, Fish, roots and cassava, yams, cocoyam-tubers, green leafy vegetables and fruits are inadequate sources of Zinc.
Inhibitors of Zinc Absorption
Although some intake of zinc may be acceptable, the level of inhibitors (fibers, phytic acid) in the diet, may mean that inadequate amounts of zinc are absorbed.
Phytates (in whole grain cereals, legumes) bind zinc in the intestines and prevents zinc from being absorbed. Iron and calcium also do interfere with zinc absorption from the gut.
Enhancers of Zinc Asorption
Protein meal, (animal and legumes) improve zinc absorption from the small intestines
DAILY ZINC REQUIREMENTS. The daily requirement: According to the US FDA,
Adult Men need 11mg/day, Adult women need 8mg/day of Zinc. Infants less than 6months need 2mg/day; 7months-3 years:3mg/d; 4-8 years: 5mg/d, 9-13 years 8mg/d, teenagers take adult recommendations.
Vegetarians and all those with risk factors for Zinc deficiency may take 150% of the recommended daily requirements.
Taking more than 50mg zinc a day on regular basis requires adding copper supplements, 2mg copper/day to prevent copper deficiency
ZINC DEFICIENCY IN THE NEWBORN/early childhood
Newborn babies need zinc to stay healthy.
To ensure adequate concentration of zinc in breast milk, the zinc transporter, ZnT2 helps move zinc from the circulation, into zincosomes in the breast. Mutation in ZnT2, leads to a much lower zinc concentration in breast milk. Newborns, solely fed on low zinc breast milk develop:
. Growth retardation
. Diarrhea and other infections
. Contact dermatitis around the mouth, anus and the limbs.
This clinical condition known as Acrodermatitis Enteropathica, (AE).
AE can also result when Zinc is not absorbed in the intestine, due to mutations in intestinal zinc transporter, human Zinc/Iron regulated transporter-like Protein (hZIP4).
AE, resolves with zinc supplementation. If left untreated, Kids with AE die in the first few months of life.
KWASHIORKOR AND ZINC DEFICIENCY.
Kwashiorkor children have lower serum Zinc levels, compared with those with Marasmus.
Zinc levels are lower in kids with protein-calorie malnutrition, than in controls.
There is a graded decrease in zinc levels from PEM grade I to PEM Grade iv.
Zinc supplementation hasten recovery and ensures adequate growth and improvement in cellular immunity for malnourished children.
ZINC DEFICIENCY AND VISION
Zinc plays a role in transporting vitamin A from the liver to the retina for melanin production. In the eyes, zinc is concentrated in the well vascularized retina and choroid tissues.
Zinc supplementation has been found to slow down the progression of age-related macular degeneration.
Zinc deficiency has been linked to Impaired vision including poor night vision, cloudy cataracts and loss of eyebrows and eyelashes
ZINC DEFICIENCY AND FUNGAL SKIN INFECTION.
Pityriasis Versicolor is common in warm and humid climates. Zinc deficiency promotes the growth of skin fungi.
Eating foods high in Phytic acid, such as Corn products and Beans, promote fungal growth. Phytic acid binds to Zinc in the small intestine, blocking zinc absorption into the circulation
Consumers of corn/maize, cassava food, need to take zinc supplements to avoid zinc deficiency and catching Tinea Versicolor.
ZINC AND PROSTATE CANCER
Normal prostate gland, has the body’s highest concentration of Zinc.
Zinc transporters (ZIP1) are very active in healthy prostate epithelial cells. In cancerous cells, the transporters become silent, leading to reduced zinc influx. Prostate cancer cells have only a third of the zinc concentration, compared with healthy cells.
The high zinc concentration in prostate cells, is needed to block oxidation of citrate.
During neoplastic transformation, zinc-accumulating, citrate-producing normal prostate cells are metabolically transformed to citrate oxidizing cells that lose the ability to accumulate zinc.
In the prostate cells, such a high concentration of zinc becomes toxic to the cancerous cell, but not for healthy prostate cells.
Resveratrol, (antioxidants in cocoa beans, grapes and other plant foods) increase Zinc transport into the prostate gland.
Research still ongoing, but it is anticipated that a combination of daily cocoa consumption (for resveratrol) and zinc supplements could go a long way in impeding prostate cancer development
For now, men over 40 years of age, must consider taking zinc supplements and cocoa products, daily.




 Akufo-Addo commissions Phase II of Kaleo solar power plant
Akufo-Addo commissions Phase II of Kaleo solar power plant
 NDC panics over Bawumia’s visit to Pope Francis
NDC panics over Bawumia’s visit to Pope Francis
 EC blasts Mahama over “false” claims on recruitment of Returning Officers
EC blasts Mahama over “false” claims on recruitment of Returning Officers
 Lands Minister gives ultimatum to Future Global Resources to revamp Prestea/Bogo...
Lands Minister gives ultimatum to Future Global Resources to revamp Prestea/Bogo...
 Wa Naa appeals to Akufo-Addo to audit state lands in Wa
Wa Naa appeals to Akufo-Addo to audit state lands in Wa
 Prof Opoku-Agyemang misunderstood Bawumia’s ‘driver mate’ analogy – Miracles Abo...
Prof Opoku-Agyemang misunderstood Bawumia’s ‘driver mate’ analogy – Miracles Abo...
 EU confident Ghana will not sign Anti-LGBTQI Bill
EU confident Ghana will not sign Anti-LGBTQI Bill
 Suspend implementation of Planting for Food and Jobs for 2024 - Stakeholders
Suspend implementation of Planting for Food and Jobs for 2024 - Stakeholders
 Tema West Municipal Assembly gets Ghana's First Female Aircraft Marshaller as ne...
Tema West Municipal Assembly gets Ghana's First Female Aircraft Marshaller as ne...
 Dumsor is affecting us double, release timetable – Disability Federation to ECG
Dumsor is affecting us double, release timetable – Disability Federation to ECG
