In this article I would like to talk about issues that are at the top of the agenda in international politics currently especially from the major power countries and the regional powers, I got it after watching a movie in mid-2018 called the Red Sea Operation(Operation in the Red Sea) by the Chinese navy. The film explores China's determinations and ambitions to play a leading part in the World politics and to play a foremost role. I also sparked to my mind by a brief article that I posted on my Facebook page which I named as ‘‘All Veto Powers stand at the threshold of the Horn of Africa’’.
In the Second World War, two major powers emerged as leading the world in eastern and western politics, it was at the forefront of the policy in the Eastern European countries by the then USSR and its allies WARSAW which flies to the far right of the socialist system, Whereas the western world was led by the US and its NATO allies, these were embedded in the political imagination of capitalism (Capitalism view).
These powers became the victorious countries that won the Second World War. An immediate territorial competition emerged, with each party expanding its thinking and each wishing to gain more countries and allies to join and sell their approach on the basis of systemic policies. The high demand for these forces is the result of what is known as the cold war. This system cold war policies have clearly been bias to the leaders of the two powers which of course the United States and Russia,
The concentration of these large countries has led to the use of smaller countries with one against another, which has created a dangerous perception of war in smaller countries or what it internationally known proxy wars.
Beginning in the late nineteenth in twentieth century, a great Soviet country a power that was a thrust of the eastern society had disappeared the Warsaw alliance collapsed, with most of the Eastern European countries plunged by conflict at the height of the Balkan War. The issue of destructive civil wars in Eastern Europe presents an unprecedented opportunity for NATO allies, especially the United States and its leading allies. Eliminated much of the attention and resources that the West has spent on intelligence operations. The strategy and funding of the various armed forces, in particular reduced the budget for foreign policy in those countries.
Similarly, the collapse of the Soviet Union made it possible for smaller countries that had previously joined the Russian alliance to join the only existing forces in this time NATO and at the same time adopt the traditional capitalist system.
Many of these communities are supported in administrative reforms, Government agencies and infrastructure funding by Western countries which they adopted in their vision the emergence of the democratic system, this has led to economic optimism and revitalization for people breathing previously under the socialist system. And the countries of the Horn of
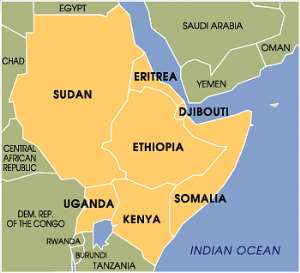
Africa are no different from the aforementioned Eastern European countries. Asia, the Middle East and the Red Sea have been central to the strategic and friendly expansion of the struggled superpowers.
The collapsed republic of Somalia has joined the Eastern bloc, where the revolutionary dictatorship led by General Mohamed Siyad Barre imposed on the country's scientific socialist system. Ethiopia, on the other hand, which has long been under the monarchy taken power in coup d’état by Derg With control of the country when the overthrow leader Mengistu unconditionally joined to the system of socialism that ruled in Moscow.
This change happened in East Africa comes at a time when the strategically overtaken Soviet allies in Africa and the Middle East, This time Egypt has withdrawn from Russia on a crucial site along the busy Sues Canal. Somalia and Ethiopia join USSR allies set fire to these already struggle and contest on military, commercial, political, and ideological between the two alliances and made the Horn of Africa a new site that has attracted international attention.
The collapse of the Soviet Union and the disintegration of the eastern bloc allies we said that, the US and its allies have lowered military budget that spent much of their foreign policy on private affairs, especially in the matter of intelligence.
This issue has raised awareness of another threat from the Arab world and the Horn of Africa, Jihadist youth organized many anti-Western movements, and created an environment that threatened the Western powers in the region at this time want to peacefully pursue their interests. This time the so-called war on terror has emerged and the United States is at the forefront again, many countries in the world, especially in the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and East Africa directly confronted a jihadist on one side and anti-terrorist on the other hand,
The West has had to regain and exalt its old security and political interests in overseas, and this has disrupted and divided the whole world once again. The destruction of property, the loss of souls and the new chaos that has brought the world into a frenzy (New World Disorder).
In the first half of 2018 The United States has revised its US Foreign Policy following US foreign policy and Security experts have acknowledged that the US anti-terrorism policy has led to a recession on economy and strategically disrupted and created hater for its citizens in the world. At the same time, the United States has led to a major setback in world leadership, and it has been necessary to reform its foreign policy and thereby eliminate the war on terrorism policy by replacing it with a geopolitical strategy.
Although the Horn is one of the world's most dangerous places, its geographical important location has made it a place of considerable interest to politicians, intellectuals, commentators and political analysts and diplomats in general.
Let me return to the purpose of this article as a response to the question we began with the discussion of this article. What is all about rivalry in the Horn of Africa?
Of course this question is so extensive that it needs to be subjectively debated and investigated in all its dimensions, I think that, one, two articles we can't summarize, but it is important to address and make a few key points about the underlying causes and motives behind the conflict in the Horn of Africa and the middle east states that you seem to be all the same in recent times (One Block) when in discussing the similarities things twined the two regions.
Three factors are the basis for why the Horn and the Red Sea are becoming the most competitive and rivalry place where fierce competition reaches at its height.
- Strategic and Military Competition:
The collapse of the Great Russian country paved the way for the People's Republic of China to join in lobbying for international policy and public appearances. Economic growth in this country after changes in China's closed-door trade policy has moved to open market policy (Free Market) leading more than 800 million Chinese nationals out of poverty to join the high- income community. The small factories and the cutting edge of the Chinese people knowledge have made this country a great respected nation. For more than a decade China has invested heavily in the Armed Forces, mainly China Navy.
The main reason for the financing of the navy was to protect large shipments of Chinese exports to the Gulf and African countries, as well as the bulk of the imported oil through the busy maritime route of Bab el-Mandeb (Bab el-Mandeb Strait). This has forced China to make friends in the horn and on the Red Sea countries in order to expand its trade and military force.
China has a Navy base in Djibouti for the first time in its history. This has brought fear to the West and has caused the United States to change its political outlook (Reshaping US foreign policy). This makes the Horn of Africa a fierce political geographical contest between major powers. Bab el-Mandeb’s busy maritime route in the Red Sea has made it an open battle for competition in the world's most economically and militarily powerful countries.
This time, the United States returned to the Red Sea and the Horn of Africa with Camp Lemonnier which was originally established as garrison for French foreign Legion the base was leased by Djibouti to the United States in 2001, along with the right to use the neighbouring airport and port facilities. Where France, Japan already had military bases and expanded its political access and military support to the horn.
At the end of the first decade in twenties first century, the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean has begun a fighting against piracy after severing merchant ships encountered insecurity at the waters off the Indian Ocean.
A number of ships were hijacked and officers and sailors aboard were demanded ransom to regain their freedom. The issue of piracy has prompted major powers and many other allied countries to intervene in the security situation that is at the heart of the most important trade route between the western and eastern parts of the world.
This has offered opportunity to China, Russia and others who have missed out on the Horn of Africa and the Red Sea. More than forty-four countries (44) have joined the anti-piracy mission in the Indian Ocean and offshore Somalia. For the first time, the European Union Mission in Djibouti has been at the centre of operations (European Union Capacity Building Mission) that against acts of piracy and human trafficking. After a long period of neglect, the Horn of Africa has again become the target of the West and to some extent the rest of the world.
Turkey has taken control of the island of Suwakin in Sudan and the step taken by Turkish has forced the United Arab Emirates and the Saudi Arabian side to form a military base in Assab, Eritrea.
Eritrean leader Isaias Afwerki has received massive financial support from the Saudi Arabia and United Arab Emirates, which has helped to secure the country's economy on the hand. This two regional Middle Eastern nations played as well an important rule to negotiate Eritrea and Ethiopia which have been enemies in long time and wiped out the stalemate between two brotherly nations.
On the other hand, it is no less than Ethiopia after the UEA handed over more than three billion dollars in loans and grants to Ethiopia to recover from the recession and cash shortages caused by the upheavals and political unrest that overthrown The ruling EPRDF (the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front) from the power which was the strongest associates arm of the ruling TPLF (Ethiopian People's Liberation Front).
- Trade and Economic Competition;
The production of oil in the Middle East, especially in the Gulf, has led to the emergence of more regional hegemony in the field of foreign policy, military power and international trade. The economic growth of oil-rich natural resources in the Gulf countries has allowed them to expand their influence on the Red Sea and the Horn of Africa.
The rapid population growth of the African continent (250 Million 1950 to 1.2 Billion in 2019) has made the continent a competitive place. The Horn of Africa, the world's gateway to the continent of Africa, has given countries in the Gulf, China, Turkey and other East Asian countries the opportunity to attract more customers to sell their goods and products.
The United Arab Emirates, which is the leading Saudi Arabia's allies in trade policy, has now expanded its business influence on the African continent, especially in the Horn of Africa. UAE- based Dubai Port World (DP World) has led the expansion of the UAE, with an agreement with Djibouti for the expansion and modernization of the port of Djibouti.
Prevalent clash between Djibouti and the Emirate has led to the cancellation of the agreement, which immediately diverted the DPW port's plan to Berbera port in Somaliland. A subsidiary company of DPW also entered into an agreement with the regional administration of Puntland to operate the port of Bossaso, and the port of Kismayo was leased to the UAEn as well.
The departure of DP World at the ports of Djibouti provided a great opportunity for the Chinese nation, who had recently made their way to Africa. China had found easy access to the ports of Djibouti, a tiny nation in strategic location. The agreement between the Djibouti and China for ports is heightened by the enthusiasm for the Horn of Africa in terms of trade, military, and political contact.
On the other hand, Turkey has taken over the port of Mogadishu and Adan Adde Airport. Turkey's ambitions on long-term policies go back to 2011 when the time Turkish Prime Minister currently president Rajib Erdigon visited to the capital Mogadishu as a result of the severe drought traumatised Somali people, Turkish aid and its humanitarian aid organizations generosity to Somalis have made Turkey and the Somali government close friends. This gave Turkey the opportunity to express itself on the political front and on its future trade with Africa.
It was recently when nine million dollars on Emirate private jet was seized by Somali Government at Mogadishu's Adan Adde International Airport. Although the UAE has claimed that the money was going to its own forces in Mogadishu, The Somali government argues that the money was illegal and instead was to finance violent activities in Somalia which later Somalia takes over the money.
The capture and seizure of this money resulted in a diplomatic explosion as the United Arab Emirates withdrew its forces in Mogadishu and halted humanitarian aid to the Somali people. The urgency and sophistication of the UEA-led coalition, which is Emirates think as the strategist in its approach, shows that they have no vision and a plan to guide their strategic future aspirations.
The Emirate has established a military base in Somaliland, to replace Mogadishu and has promised to convert Somaliland for construction a corridor between Berbera's main port and the Ethiopian border. Turkey and Qatar as well as, Iran on the one hand, and Saudi Arabia, the Emirate and Egypt, on the other hand, intervene starkly in countries across the Horn of Africa to pursue their economic and political interests.
- Competition of Principles and ideology:
Religious and ethnic diversity has made the Horn of Africa the most violent spot in Africa and in the world. The spread of ethno-religious principles has had a negative impact on the progress of countries in the Horn by creating internal and external conflicts (Inter and intra- state war).
The economic upheaval in the Gulf and Iran and Turkey has led to a sectarian crisis that has intensified in the wake of Shia and Sunni sectarianism as the region continues to expand.
The Wahabi school of thought and it’s ideology that founded back at eighteen century in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia has largely influenced the lives of thousands of young people who learnt across the Gulf countries and returned to other Muslim countries to spread their philosophy especially in Somaliland, Somalia, Djibouti and Sudan, and even Ethiopia where they established wahabi denomination in Sunni ideology. These views are often contradicts
with the system of government in predominated Muslim nations in the Horn. The Arab Spring revolution has led to the emergence confrontation between Wahhabi and Shia movement in the region. This has come to the peak after Saudi Arabia supports the war against Syrian leader Bashir al-Assad. On the other hand, Iran has offered support for the large Shia of Bahrain to take control over the small Sunni realm.
However, the issue of extending religious principles and the influence of foreign extremism, which now appears to be widespread, took a sharp turn to the Horn of Africa when the civil war broke out in Yemen and beyond the Horn.
A coalition of countries including the Middle East, Sudan and the Pakistani government led by Saudi Arabia has begun fighting in Yemen to put an end to the insurgency Hutthi Rebels.
This war reveals the conflict between Sunni and Shiites believes and the political and military row between Iran and Saudi Arabia that depends on the interests of the Middle East and the Islamic world and who leads the control of the precious Red Sea and Humus routes.
In terms of diplomacy, Saudi Arabia has donated $ 50m to Somalia in January 2016 in replace that to cut ties with Iran, Somalia government has immediately accepted the offer from the kingdom and cut ties with the Iranian diplomatic relation and closed the doors of Iran embassy in Mogadishu.
On the other hand, the Sudanese regime leader, who had recently descended from the power by civil unrest Omare Al Bashir, offered to cut ties with the Iranian alliance, after which he received diplomatic and economic rewards from the Gulf countries.
In the countries of the Horn of Africa there are widespread divisions between communities in these countries, divided by ethnic and religious ideology. Ethiopia, the country with the highest number of people in the Horn of Africa has become the most negatively impacted country in terms of ethnic and religious segregation as this country is divided between Islam and Christianity.
This has made the countries of the Horn always open to their divisiveness for foreign interference, in which countries export their ideas and principles.
What do the Leaders of the Horn of Africa Countries perceive from rival for their region?
According to a report by Professor Paul Williams, a professor in international affairs at Elliot University, more than 1500 conflicts have occurred in Africa after 1991 with more than 400 disasters happening in countries across the Horn of Africa Making it more than any other region in the world compared to the horn.
High levels of migration, immigration, crises, insecurity, poverty and ignorance have made the region of the Horn of Africa largely fragile. Climate change, recurrent droughts and wars have left much of the population in the Horn of Africa at risk. Poverty and unemployment in these countries have resulted to young people and future generations becoming refugees in Western Europe and the Middle East.
Hundreds of young people looking for a better life out of their home countries die each month on the long journey between death and life. Many young migrants have died at sea and in the desert, while others are being held hostage in North Africa.
According to Alex De-Wall, author of the book Real Politics of the Horn of Africa (The Real Politics of the Horn of Africa: Money, War and the Business of Power). The influx of huge amounts of money by the Gulf nations, Western and international investment institutions in the Horn of Africa has led to demands and calls from foreign investors to carry out their interests in the Horn.
on the contrary, the leaders of the Horn of Africa countries maintain their dominance by ignoring the interests of their people and the right leadership of the region that would lead to a better tomorrow for future generations and peoples living in these countries.
In the context of a combination of problems, poor governance and widespread dysfunctions, most of the countries dominate making this region more vulnerable to foreign policy and military interference, it is important that leaders and intellectuals from these countries provide a lasting solution to the retrograde in these countries which is a key step forward How do political leaders implement them.
Bringing lasting and sustainable solutions can be based on:
- Inclusive Participation in politics:
The reorganization and reformation of government institutions, political participation and inclusive consultations provide opportunities for the development of social, good governance and security in and improves the fates of millions living in the horn of the country.
The impact of these activities could lead countries in Sudan and Eritrea, Djibouti and Somalia to change their domestic policies that now need to be reviewed. There are still in Sudan need to find a way to end the civil war and Eritrea should create incentives in the country policies so that young people choose to stay at home rather than migrate.
The lack of citizens' participation in politics in which they feel their fate is not in the hands of anyone else is a primary challenge. This has several points on how we understand and define democracy, how young people and women participate in political deliberation, how to rebuild a nations, and how to best distribute resources and share natural resources in the region evenly.
- Integration on Economic and political in the regional states:
Creating a collaborative environment on economic, political and security cooperation produces opportunities for mutual trust between the countries and increases community integration and the growth of the vision of regional leaders.
Winning sustainable economic cooperation in the region can benefit from the strong arm, the muscle and the brain, especially in the potential of youth and the abundant natural resources in the seas and on land that have not yet taken advantage of the most appropriately.
If the leaders in the horn of Africa succeed in creating a co-operative environment, surely they will defeat and take the position for any foreign and domestic forces who are indispensable interfere to the Horn of Africa.
From a regional perspective of distrust, regional disintegration and regional conflicts, the absence of peace in the Horn of Africa can lead to a long and complicated history of economic, political, state-building and social integration.
Written By: Saeed Hashi
Analyst for Politics, Democracy, Economy and Peace in the Horn of Africa and the Middle East




 NPP Performance Tracker prioritise toilets over substantive infrastructure dev’t...
NPP Performance Tracker prioritise toilets over substantive infrastructure dev’t...
 Ghana, other election bound-countries must build fiscal buffers – IMF admonishes
Ghana, other election bound-countries must build fiscal buffers – IMF admonishes
 Parliament reconvenes late May, denies Speaker Bagbin delaying recall over NDC t...
Parliament reconvenes late May, denies Speaker Bagbin delaying recall over NDC t...
 $100m needed to revitalise Ghana's poultry sector — GNAPF
$100m needed to revitalise Ghana's poultry sector — GNAPF
 Driver arrested for causing train collision on Tema-Mpakadan Railway Line
Driver arrested for causing train collision on Tema-Mpakadan Railway Line
 Police grab trucker for Tema-Mpakadan rail accident
Police grab trucker for Tema-Mpakadan rail accident
 Gov't plans to revise traditional customs following Gborbu child marriage
Gov't plans to revise traditional customs following Gborbu child marriage
 Franklin Cudjoe fumes at unaccountable wasteful executive living large at the ex...
Franklin Cudjoe fumes at unaccountable wasteful executive living large at the ex...
 I'll 'stoop too low' for votes; I'm never moved by your propaganda — Oquaye Jnr ...
I'll 'stoop too low' for votes; I'm never moved by your propaganda — Oquaye Jnr ...
 Kumasi Thermal Plant commissioning: I pray God opens the eyes of leaders who don...
Kumasi Thermal Plant commissioning: I pray God opens the eyes of leaders who don...
