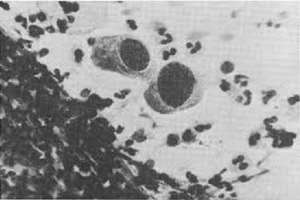
Comparisons between photos of the Cytomegalovirus and mucosis fungoids of the Dutch researcher Elisabeth van der Loo and retroviruses causing AIDS described by those of the current leading generation of scientists show almost no difference, although they want us to believe otherwise.
All retroviruses that cause Aids are "look-alikes" of the herpes Cytomegalovirus CMV (see photo bird eye cells), discovered by Germans von Ribbert and Jesionek and published in the German magazine "Münchener Medizinische Wochenschrift" in 1904.
German colleagues from von Ribbert also extensively published in the twenties and the thirties of the last century on the use of the CMV virus as a bio-weapon.
References:
Ribbert H. (1904) Ueber protozoenartige Zellen in der Niere eines syphilitischen Neugeborenen und in der Parotis von Kindern. Zbl All Pathol 15:945–948
Jesionek A, Kiolemenoglou B (1904) Ueber einen Befund von protozoenartigen Gebilden in den Organen eines hereditar-luetischen Foetus. Muenchner Med Wochenschr 51:1905–1907.
Lòwenstein C. (1907) Ueber protozoenartige Gebilde in den Organen von Kindern. Zbl Allg Pathol 18:513–718.
Von Glahn WC, Pappenheimer AM (1925) Intranuclear inclusions in visceral disease. Am J Pathol 1:445–465.
Lipschutz B. (1921) Untersuchungen Ueber die Aetiologie der Krankheiten der Herpes genitalis. Arch Dermatol Syph 136:428–482.
Luc Montagnier the pseudo discoverer of the AIDS virus: “The Cytomegalovirus identical to EIAV”
To complicate matters, Luc Montagnier discovers that the CMV virus is completely identical to the Equine Infectious Anaemia Virus EIAV of horses! And we know from that virus that it causes 'Horse-Aids'.

Cytomegalovirus with the well-known bird eye cells
The research by Montagnier also shows that the virus has the same characteristics as goat, cow, monkey, pig and human Aids-causing virus. Montagnier thus fits in seamlessly with the work of Von Ribbert and his German colleagues and especially with the CMV study by Lipschutz (1921).
References:
Luc Montagnier In; Annals of Virology: “A new type of retrovirus from patients presenting with lymphadenopathy and acquired immune deficiency syndrome”: Structural and antigenic relatedness with Equine Infectious Anemia Virus EIAV (horse Aids), 1984; 135E: 119-31.
Lipschutz B. (1921) Untersuchungen uber die Atiologie der Krankheiten der herpusgruppe. Arch. Dermatol. U Syph.: 428-482.
Third Race Betterment 1928
All scientific investigations in the field of herpes and retroviruses in that early period are ultimately expressed in; "The Third Race Betterment Report", improving the third race, a eugenics program of the Nazi's and their predecessors, with which, according to their sick mind, inferior people like Jews, Negroes and Gypsies can be eliminated. Many diseases have emerged from these medical experiments and so have AIDS.
The squabbling of the current generation of researchers such as Robert Gallo (HTLV-1), Luc Montagnier (LAV) and the Japanese Hinuma, Takatsuki, and Miyoshi (ATL), who claim the discovery of AIDS is based solely on deception, the drive for power, prestige and especially for the Nobel Prize.
And these researchers, in their drive for fame, have never done truth-finding in the interest of the "Dissertation Machine".
Ref: Third Race Betterment 1928
https://wellcomecollection.org/works/ex9tb25e
https://searchworks.stanford.edu/view/539563
http://www.eugenicsarchive.org/html/eugenics/static/themes/19.html
The origin of the AIDS virus took place in the aforementioned time frames and this is now increasingly confirmed by scientists and whistleblowers who lean towards the green group. That are scientists who are investigating fiction and uncovering unimaginable medical crimes against humanity.

Equine Infectious Anaemia Virus EIAV Is Similar To HIV
No less than Luc Montagnier, the discoverer of the HIV virus stated that this virus is made out of the Nazi eugenics and genetic engineered experiments during the second world war as well as the development of Aids causing viruses in horses.
In a much-discussed scientific article, Montagnier describes his findings in the leading medical journal; Annals of Virology: "A new type of retrovirus from patients presenting with lymphadenopathy and acquired immune deficiency syndrome": Structural and antigenic relatedness with Equine Infectious Anemia Virus EIAV (horse AIDS), 1984; 135E: 119-31.
The scientific literature also shows that EIAV and HIV are completely identical to the monkey virus Simian Immunodeficiency Virus SIV.
References:
In a much-discussed scientific article, Montagnier describes his findings in the leading medical journal; Annals of Virology: "A new type of retrovirus from patients presenting with lymphadenopathy and acquired immune deficiency syndrome": Structural and antigenic relatedness with Equine Infectious Anemia Virus EIAV (horse AIDS), 1984; 135E: 119-31.
Below the comparison between the human HIV and monkey virus SIV

Human HIV virus

SIV virus
The scientific literature also shows that EIAV and HIV are completely identical to the monkey virus Simian Immunodeficiency Virus SIV.
References:
Wolff Geisler, Aids, Origin, Spread, and Healing. Amazon.
https://www.amazon.com/Origin-Spread-Healing-shortened-version/dp/3980388328
https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/1159147.The_River_
https://secretsofaidsandebola.blogspot.com/search/max-results=8?q=SIV
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/2003/06/news-hiv-aids-monkeys-chimps-origin/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5198506/
Pseudo discoverers of the AIDS virus Luc Montagnier and Robert Gallo and
Gallo's so-called discovery of the century
A researcher who came into the picture frequently at the start of the AIDS era was the American virologist Robert Gallo. During the seventies and eighties, he frequently published on cancer and AIDS.
When a disease was reported on the Japanese island of Kyushu in 1976, Gallo was naturally directly interested in an extremely macabre yet unknown form of leukemia among humans. The discoverer of the disease, Kiyoshi Takatsuki, described in an article in Excerpta Medica how he and his colleagues from The University of Kyoto had noticed that a disease that had previously been classified into seven different diseases, and with it also led to a confusing series of diagnoses could be traced to an infection of human T cells that caused flower-shaped cell nuclei. The Japanese named this disease Adult T-Cell Leukemia (ATL) and immediately started trying to find the cause of the disease, but did not succeed.
Reference:
Takatsuki K. Discovery or Adult T-cell Leukemia (2005). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC555581/
Yorio Hinuma
Another Japanese virologist, Yorio Hinuma, who came to work at the University of Kyoto in 1980, was convinced that the blood cancer was caused by a virus, but could not prove it yet.
Reference:
Yoshida M, Miyoshi I, Hinuma Y. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6979048
Robert Gallo a snake in a bucket with snot
When Gallo, who was affiliated with the National Institutes of Health NIH in Bethesda, examined the blood of a twenty-eight-year-old African American who suffered from lymphoid skin cancer, mycosis fungoids, he isolated a virus that was clearly retrovirus. He named it Human T-cell Lymphotropic Virus (HTLV) and had a strong suspicion that leukemia in Japan might have been caused by the same virus as mycosis fungoids in his patient.
And that suspicion was correct. After the Japanese researchers had given him some serum samples from ATL patients, Gallo discovered that the virus he isolated was exactly the same as that of the Japanese. He only had to change the name of the retrovirus, without this having consequences for the abbreviation to be used.
The Human T-cell Lymphotropic Virus became the Human T-cell Leukemia Virus. And with a lot of tame, Gallo announced to the world in 1981 that he and no one else was the discoverer of the first human retrovirus, the HTLV-1. And only he has to be awarded the Nobel-Prize.
The disappointed Japanese did not trust the business and their leukemia virus continued to call Adult T-Cell Leukemia Virus (ATLV).
The stolen Nobel Prize from Elisabeth van der Loo, the modern discoverer of the AIDS virus
In a research laboratory in the Netherlands, someone was also somewhat disappointed, because in 1979, more than two years before Gallo announced his discovery, a Dutch researcher, Elizabeth van der Loo, officially the first in the world, investigated the effect of a retrovirus in T-cells in patients suffering from mycosis fungoids. She photographed the micro-organism and showed reverse
demonstrate transcriptase.
The photos were published in Virchows Archiv, but the scientific evidence that it was a retrovirus was unable to provide them because of the proliferation of blood cells did not last. Robert Gallo understood that it could not be long before Van der Loo would succeed and he knew
to keep the proliferating white blood cells alive by adding interleukins.
Reference:
Loo, Elisabeth van der, et al. C type virus-like particles specifical by localized in Langerhans cells and related cells of skin and lymph nodes of patients with mycosis fungoides and Sézary's syndrome. Virchows Arch. B. (cell. Patho.) 31: page. 428-482.

Mycosis Fungoids in accordance with research Elisabeth van der Loo
Accordingly, mycosis fungoids are equivalent to HTLV-1 and 2, ATL, EIAV, SIV and LAV. All viruses are almost certainly mutated, which means that the image of the bird's eye cells may differ slightly. However, all retroviruses are "look-alikes" and moreover correspond to the herpes Cytomegalovirus CMV, investigated by the Germans as mentioned above, that is needed together with Interleukine to develop retroviruses, to keep them alive, or to stimulate them to grow.
Since then, Gallo has been regarded as the crown prince of retrovirology and Elisabeth van der Loo remained behind as a sort of Cinderella in a failed fairy tale. Very sad that she had handed her golden slipper to the wrong prince. Crown Prince Gallo would even be king a few years later, but before that, he still had to fight a rival of the Institut Pasteur in Paris, namely; Luc Montagnier.
Gallo's second discovery of the century
Following the announcement in June 1981 of the new resistance-reducing disease AIDS by the Centers for Disease Control, an unprecedented explosion occurred in the months and years thereafter of other diseases, also associated with immune deficiency, including Kaposi's sarcoma, a very rare form of cancer that previously only occurred in older men but now also in young gay men in New York and California. It soon became apparent that the disease spread easily among homosexuals and intravenous drug users.
For two research groups that dealt with retroviruses, that was the signal for further investigation. In Paris it was Luc Montagnier's group at the Institut Pasteur and in Maryland, it was Robert Gallo's group at the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda. Both research groups initially thought that it was a new HTLV variant.
But Montagnier discovered that this new virus only grew in T4 lymphocytes and not, like the leukemia virus discovered shortly before, in T8 lymphocytes. In addition, electron microscope shots showed that the structure of the virus examined differed significantly from HTLV-I and HTLV-II.

Human T-cell Leukemia Virus HTLV-1 and Lymphadenopathy HTLV-2
Montagnier, therefore, decided to call the virus Lymphadenopathy Associated Virus (LAV). However, Gallo suspected that it was also a leukemia virus and wanted to classify it as HTLV-III. The French, however, maintained that it was not a leukemia virus, but a different retrovirus.
When Gallo examined a sample of the French virus that he requested, it turned out that LAV was exactly the same as the HTLV-III, he found. So he only had to put the old name on it again. The Human T-cell Leukemia Virus again became the Human T-cell Lymphotropic Virus and this time this did not change the abbreviation to be used for the virus.
The Human T-cell Lymphotropic Virus had been rediscovered and Gallo was second to the world in great tame in 1984 that he and no one else was the discoverer of a second "first" human retrovirus (HTLV-III). He and he alone had to be eligible for the Nobel Prize.
The disappointed French did not trust the matter and therefore continued to call their AIDS virus Lymphadenopathy Associated Virus (LAV). But Montagnier did not give up. In 1984 he published the article "A new type of retrovirus isolated from patients presenting with lymphadenopathy and acquired immune deficiency syndrome: Structural and antigenic relatedness with equine infectious anemia virus" in which he indicates that he discovered it
LAV is (almost) identical with the virus that, according to former soldiers from the two World Wars, caused horses 'that controlling Blutarmut' better known as equine AIDS.
Reference:
Luc Montagnier In; Annals of Virology: "A new type of retrovirus from patients presenting with lymphadenopathy and acquired immune deficiency syndrome": Structural and antigenic relatedness with Equine Infectious Anemia Virus EIAV (horse AIDS), 1984; 135E: 119-31.

Lymphadenopathy Associated Virus LAV
From that moment on, a fierce brotherly battle broke out between Montagnier and Gallo about who actually was the discoverer of that deadly new virus that was not at all so new. The French even decided to go to court with the Americans, because it slowly became clear that they were right on their side.
In 1987 consultations were held at the highest level between the presidents of The United States and France to appease the dispute between Gallo and Montagnier. Apparently, both nations were not helped by too much publicity about a disease that was associated with "the anti-checking Blutarmut."
The summit meeting between the two superpowers led the two fighters to stop fighting and decided to give the virus that was constantly changing its name the collective name: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). And that was a name that could in no way be related to biological warfare. And Elisabeth van der Loo and the Nazi scientists had long since disappeared.




 Tuesday’s downpour destroys ceiling of Circuit Court '8' in Accra
Tuesday’s downpour destroys ceiling of Circuit Court '8' in Accra
 SOEs shouldn't compromise on ethical standards, accountability – Akufo-Addo
SOEs shouldn't compromise on ethical standards, accountability – Akufo-Addo
 Father of 2-year-old boy attacked by dog appeals for financial support
Father of 2-year-old boy attacked by dog appeals for financial support
 Jubilee House National Security Operative allegedly swindles businessman over sa...
Jubilee House National Security Operative allegedly swindles businessman over sa...
 Nobody can order dumsor timetable except Energy Minister – Osafo-Maafo
Nobody can order dumsor timetable except Energy Minister – Osafo-Maafo
 Mahama wishes National Chief Imam as he clock 105 years today
Mahama wishes National Chief Imam as he clock 105 years today
 J.B.Danquah Adu’s murder trial: Case adjourned to April 29
J.B.Danquah Adu’s murder trial: Case adjourned to April 29
 High Court issues arrest warrant for former MASLOC Boss
High Court issues arrest warrant for former MASLOC Boss
 Align academic curriculum with industry needs — Stanbic Bank Ghana CEO advocates
Align academic curriculum with industry needs — Stanbic Bank Ghana CEO advocates
 Election 2024: We'll declare the results and let Ghanaians know we've won - Manh...
Election 2024: We'll declare the results and let Ghanaians know we've won - Manh...
