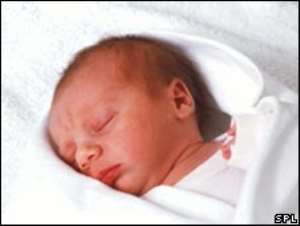
The first baby in the UK tested before conception for a genetic form of breast cancer has been born.
Doctors at University College London said the girl and her mother were doing well following the birth this week.
The embryo was screened for the altered BRCA1 gene, which would have meant the girl had a 80% chance of developing breast cancer.
Women in three generations of her husband's family have been diagnosed with the disease in their 20s.
Paul Serhal, the fertility expert who treated the couple, said: "This little girl will not face the spectre of developing this genetic form of breast cancer or ovarian cancer in her adult life.
"The parents will have been spared the risk of inflicting this disease on their daughter.
"The lasting legacy is the eradication of the transmission of this form of cancer that has blighted these families for generations."
Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) involves taking a cell from an embryo at the eight-cell stage of development, when it is around three-days old, and testing it.
This is before conception - defined as when the embryo is implanted in the womb.
Doctors then select an embryo free from rogue genes to continue the pregnancy, and discard any whose genetic profile points to future problems.
Using PGD to ensure a baby does not carry an altered gene which would guarantee a baby would inherit a disease such as cystic fibrosis, is well-established.
But in 2006, the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority said doctors could test for so-called susceptibility genes, such as BRCA1.
Everybody carries a version of these genes - in fact a properly functioning BRCA1 protein helps stop cancer before it starts - but some particular variations of the genes greatly increase the risk of cancer.
Increased chance
Carrying the key BRCA1 mutation in this family's case would have given the increased chance of breast cancer and 50% chance of ovarian cancer later in life.
However, carrying the gene does not make cancer inevitable, and there is also a chance the disease could be cured, if caught early enough.
The couple, who wish to remain anonymous, wanted to eradicate the gene flaw from their family.
The husband's grandmother, mother, sister and a cousin have been diagnosed with the disease.
If the 27-year-old woman and her husband had had a son, he could have been a carrier and passed it on to any daughters.
Josephine Quintavalle, of the campaign group Comment on Reproductive Ethics, said: "This is nothing personal towards the girl, but I think we have gone too far.
"Underlying all this is eugenics."
Mrs Quintavalle said the message was that "you are better off dead, than being born with this gene".
"I hope 20 years down the line we will have eradicated breast cancer - not eradicated the carriers.
"This testing procedure is being used more and more for less and less significant reasons."
But Kath McLachlan, of Breast Cancer Care, said those with the faulty BRCA1 gene would be very interested in the development.
"There are many complex issues to take into account before undertaking PGD, and the decision will finally come down to an individual's personal ethics."
And Professor Peter Braude, director of the Centre for PGD at Guy's Hospital in London, said: "The decision as to whether PGD is appropriate for a couple will be made after a thorough discussion with knowledgeable genetic counsellors and clinical geneticists.
"It will not be suitable for everyone who has experience of breast cancer in their family, nor where the chances of the IVF needed for PGD has a low chance of succeeding."




 Whoever participated in the plunder of the state must be held accountable – Jane...
Whoever participated in the plunder of the state must be held accountable – Jane...
 A vote for John and Jane is a vote to pull Ghana from the precipice of destructi...
A vote for John and Jane is a vote to pull Ghana from the precipice of destructi...
 I’ll repay your abiding confidence with loyalty, understanding and a devotion to...
I’ll repay your abiding confidence with loyalty, understanding and a devotion to...
 ‘I’ve learnt deeply useful lessons for the future' — Serwaa Amihere breaks silen...
‘I’ve learnt deeply useful lessons for the future' — Serwaa Amihere breaks silen...
 I’m sorry for the embarrassment – Serwaa Amihere apologises for leaked sex video
I’m sorry for the embarrassment – Serwaa Amihere apologises for leaked sex video
 Dumsor: Matthew Opoku Prempeh not in charge of Energy sector – Minority
Dumsor: Matthew Opoku Prempeh not in charge of Energy sector – Minority
 Adu Boahen’s murder: Police arrest house help who was in possession of deceased’...
Adu Boahen’s murder: Police arrest house help who was in possession of deceased’...
 Akufo-Addo nominates Felicia Attipoe as Tema West MCE
Akufo-Addo nominates Felicia Attipoe as Tema West MCE
 Election 2024: I can't have someone I defeated twice as my successor – Akufo-Add...
Election 2024: I can't have someone I defeated twice as my successor – Akufo-Add...
